
Insights
What is Bandwidth?
When it comes to broadband, bandwidth is the capacity of your internet connection or Wi-Fi signal. This is the rate at which data can be transferred over your network via your router, which will directly affect the speed of your broadband service and the quality of what you see on screen.
When you’re looking at changing your home broadband, bandwidth will be right up there as one of your primary considerations, along with cost and level of customer service.
Here, we’ll look at what bandwidth means in general terms, what you can do to get the most out of your broadband and how you can find out more about the status of your connection.

What is bandwidth measured in?
Bandwidth is measured by the amount of data you can send or receive over your broadband connection. This is stated in bits per second (bps), but with new internet lines being so much faster than before, you’ll usually see bandwidth measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Bandwidth vs. Latency
Latency is related to the quality of your broadband connection. The lower the latency, the better. While bandwidth could be seen as another way to look at your connection’s speed, latency represents the delay you might experience depending on how the data signal is passing from the network to your device. For example, a wireless connection will have higher latency than an ethernet cable between your computer and the router. Our dedicated article on latency explores the subject more thoroughly.
Bandwidth vs. Speed
While both speed and bandwidth are measured in Mbps or Gbps, there is a very subtle difference between the two terms. Broadband speed is a measurement of how fast data can travel through the connection. Bandwidth relates to the volume of data, which could be more even if it still travels at the same speed.
Imagine a log floating on a river. The log might travel quickly through a narrow river channel, but if the water and the log move at the same speed through a wider channel, your data (the log) will be travelling at the same speed, but you will have far greater bandwidth (water in the river). Therefore, room for more logs, or data.
Bandwidth vs. Throughput
Related to the last point, ‘throughput’ is a term for the amount of data that actually gets transferred from one point on the network to another in a certain amount of time. So, if bandwidth is the maximum amount of data you could receive over a certain period, throughput is a measurement of how much of that data makes it through the network after latency, speed and other external factors have had an effect.
How much bandwidth do I need?
The bandwidth you actually need for your connection will depend on the number of devices in your household, and how many will be in use at the same time. It’ll also depend on what you use your broadband for – simple browsing, social media and TV, or do you also work from home, make a lot of video calls, make heavy use of cloud-based apps or systems or enjoy interactive online gaming?
The table below shows minimum and recommended figures for bandwidth per device:
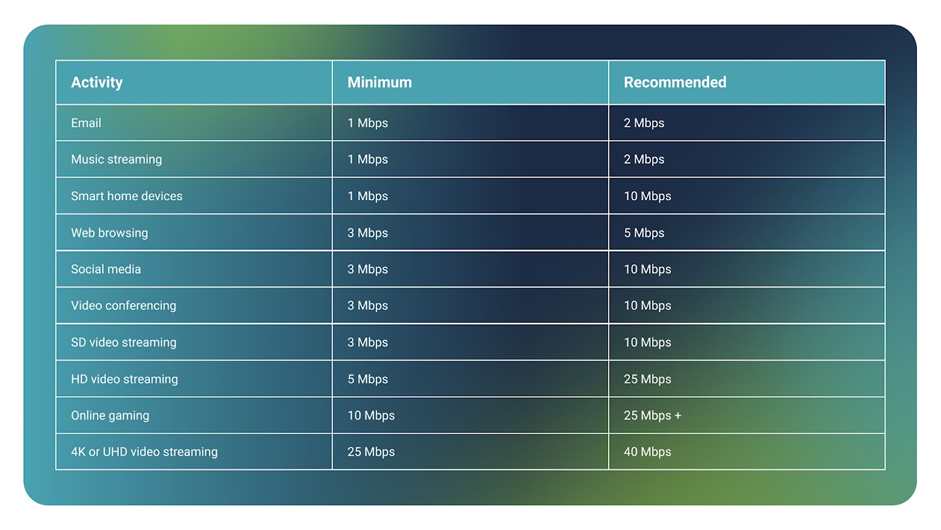
If you’re working from home and emailing, accessing the office network, making a video call, sending a large file and streaming music, you’ll need to add up the recommended figures for each activity. Likewise if you’re gaming online and streaming your progress at the same time.
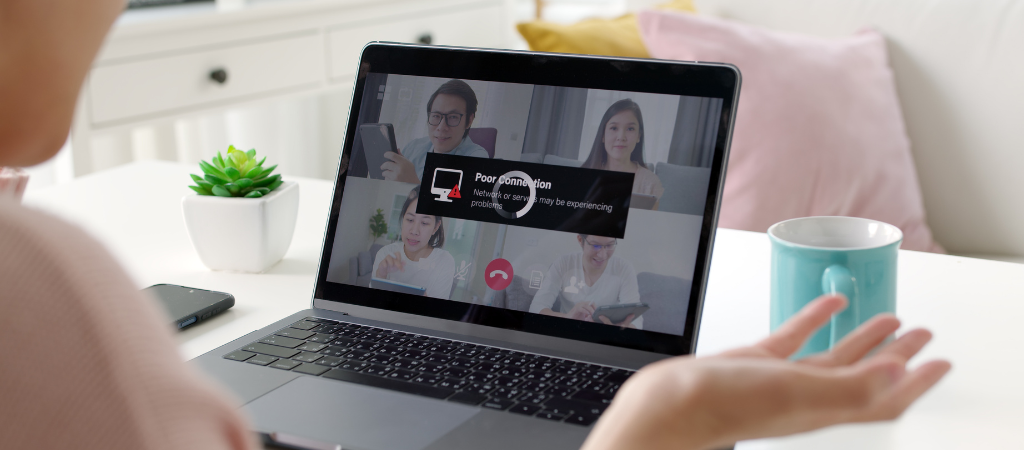
And don’t forget all the other people and devices in your home. Aside from music streaming in the background and smart devices sending information over the internet, a housemate streaming sports in HD in the next room will squeeze down the bandwidth available for your important group conference call for work or online multiplayer gaming.
Add to this your phone use for browsing, social media and facetime calls, and you could need more bandwidth for your home broadband than you think.
How can I improve my bandwidth?
Here are a few tips to improve your bandwidth, most of them being simple common sense measures to ensure you make the best use of your home broadband connection.
Use a wired connection
This is a simple trick that most forget about. If many devices are connecting to your router wirelessly, then this will naturally squeeze the available bandwidth. If you physically connect your device with an ethernet cable, the signal travels through that dedicated line, making your connection faster and more efficient (as well as allowing more wireless bandwidth for other devices).
Limit the number of connected devices
Similarly, if a lot of gadgets are using the same broadband connection, this will reduce your bandwidth for each. Perhaps turn off or disconnect any that you don’t need, or ask other family members to avoid gaming or downloads at certain times to allow you to get the best possible bandwidth for your activities.
Clean up your devices
You might not know it, but multiple applications could be operating in the background, sending and receiving data, and taking up more bandwidth than necessary. This is especially true if one or more computers have been infected with malware that could be spying on your online activity or using your devices for processing. Run a malware detection program, clear caches, update your security, close unused applications and clean up your disc space.
Upgrade your router
If you’ve had the same router for a few years, chances are that it simply isn’t equipped to handle the bandwidth you need from it, especially if you have multiple users in your home. You might get ultrafast broadband arriving at your house or flat, but with a poor router you might only get 30 Mbps by the time your device interacts with it. Always make sure your router is positioned centrally in your home and reboot it regularly to reset what it’s doing.
Upgrade your broadband plan
Perhaps the simplest measure, if within your budget, is to buy more bandwidth with the next level of service from your provider. Or perhaps switch providers if your current supplier is unable to meet your needs to one with a network that can.

How do I monitor my network bandwidth?
It’s useful to know how much bandwidth you are actually using on a daily (or sometimes hourly) basis. This way, you’ll know the kind of package you’ll need from your provider – preventing you from spending more than you need or getting hit with lag and degraded signal during use.
Sign up to third party tools
A network analysis app like GlassWire or Capsa can monitor your internet usage in real time and provide detailed information about data transfer. This can be broken down into which devices, websites and applications are sending and receiving data.
Use your router’s interface
Most routers these days will include built-in tools and a downloadable dashboard for you to access and customise settings for your broadband connection, as well as monitor your bandwidth and data use. As your router processes all information about the traffic coming in and out of your home via the internet, it will have the most comprehensive overview. Log into it via your browser, following any instructions that came with your router and entering your IP address. In addition to monitoring your bandwidth usage, you can also remove unwanted or unnecessary devices from your network, freeing up more bandwidth for others.
Conclusion
Bandwidth can be a deciding factor when it comes to choosing your next home broadband package. The level of bandwidth you might choose will depend on how many people and devices are connected to the internet, and what you use it for.
At Jurassic Fibre, we’re happy to talk to customers and communities in the South West region about all aspects of their broadband experience and the bandwidth people can expect – wherever they are or whatever devices they are using.
Feel free to get in touch with our customer service team – all based locally in Exeter. You’ll get answers to all your questions.
Latest news
A network for the future
Why Jurassic Fibre?


